SPEAKER NOTES OF CLINICAL COMPLEXITY IN PULMONARY EDEMA
SPEAKER NOTES FOR CME ON JAN 25,2023
Good afternoon everyone I am Hyndavi Konakanchi intern in kamineni institute of medical sciences
I WOULD LIKE TO SHARE MY EXPERIENCE WITH A CASE OF COMPLEX PULMONARY EDEMA
PPT SLIDES AND THEIR RESPECTIVE SPEAKER NOTES :
SLIDE NO.1
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.1
The complaints of the 62 yr old male presented to casuality at 4 pm in the evening are difficulty in breathing even at rest , cough with expectoration , bilateral pitting type of pedal edema
SLIDE NO.2
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.2
Pt was apparently normal 30 yrs back , then he had burning sensation in the feet for which he went to hospital , there after doing the necessary investigations he was diagnosed to have type 2 DM and HTN with 150/100 mm Hg and from then he was on metformin ( for 27 yrs ) and amlodipine 10 mg
5 yrs back he had urinary tract infection with renal calculi, for which he underwent lithotripsy , and post surgery was uneventful.
SLIDE NO.3
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.3
After 8 months of surgery, pt had fever, general weakness for which he went to a hospital; investigations were done and found to have rised creatinine of around 1.6 - 2.0, for which he was prescribed tab.uremax & tab.nodosis , he used medications for 5 months & again when his creatinine levels came to normal he used to stop the medications for 1 month and this cycle was continued till date
3 yrs back he again developed burning sensation of feet and fatigue went to hospital at Nalgonda , where he was adviced insulin 30u morning— 15 u night USED FOR 1 YR ; but still his sugar levels are uncontrolled so changed to mixtard 20 u morning — 15 u night till date ie 2 yrs. And along with insulin he was also on gliclazide extended release tablets 60 mg
3 yrs ago he had left hand weakness and mouth deviation, slurred speech MRI BRAIN was done and diagnosed to have ? Infarct ,then he was prescribed medication ecospirin
SLIDE NO.4
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.4
2 yrs ago he had an episode of epilepsy and was advised anti epileptic drugs then
SLIDE NO.5
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.5
He was k/c/o Diabetes type 2 and was on metformin for 27 yrs , mixtard insulin and gliclazide for 3 yrs , HTN and was on amlodipine 10 mg for 30 yrs
SLIDE NO.6
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.6
On General examination ; pt was conscious , coherent and cooperative
He was well oriented to time, place, person
There is b/l pitting edema present & no pallor,icterus,cyanosis,clubbing,lymphedenopathy
On presentation his vitals were :
Bp was 130/60 mm Hg
Pulse rate was 95 bpm
Respiratory rate was 35 cpm!!!
Spo2 was 75 % under RA and 91 % under 8 L of O2
SLIDE NO.7
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.7
He is having truncal obesity which is responsible for his diabetes
Mechanism : adipose tissue in obesity is responsible for the release of Adipokines, FFAs mediates inflammation causing insulin resistance; in response to this there is compensatory mechanism of beta cells of pancreas ; they start producing more and more insulin and at one point of time beta cells fail to produce insulin leading diabetes
Diabetes can cause LVH
Mechanism : diabetes causes AGEs (advanced glycation end products) accumulation causing ECM (Extra Cellular Matrix ) remodelling , myocyte apoptosis—fibrosis—LV CONCENTRIC HYPERTROPHY
SO IT IS EVIDENT THAT ; THE MAIN CULPRIT HERE IS TRUNCAL OBESITY
SLIDE NO.8
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.8
Systemic examination ; Respiratory system : on inspection chest is bilaterally symmetrical , on palpation trachea is centrally placed & chest movements were symmetrical on both sides , on percussion there is resonant note, on auscultation diffused wheezes and crepts in left and right sides of chest
Cardio Vascular system : s1,s 2 present
Central Nervous system : no focal neurological defect
Per abdomen : soft, non tender and bowel sounds present
SLIDE NO.9
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.9
These are the sequence of x rays done on consequetive days of recent admission at our hospital initially showing bilateral perihilar homogenous opacities which resolved over a span of 5 days and also pt started feeling better symptomatically
THE DIFFERENTIALS OF THESE OPACITIES COULD BE DUE TO: pulmonary edema secondary to heart failure or infection like pneumonia
So, opacities noted in xray can be attributed to pulmonary edema due to heart failure rather than infection like pneumonia because the span of recovery is shorter , obviously pneumonia cannot be resolved in 4-5 days it will take approximately a month to resolve.
SLIDE NO.10
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.10
ECG showing sinus rhythm , P wave normal , R wave in V4, V5, V6 is more than 25 mm — matches framingham criteria of LVH
SLIDE NO.11
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.11
2d echo report also showed LVH and diastolic dysfunction, and EF of 58% ( HF p EF )
MECHANISM BY WHICH PATIENTS OF LVH LANDS IN FAILURE CAN BE EXPLAINED BY LAPLACE LAW: WHICH DENOTES P= 2T/ R ( where P is pressure inside the left ventricle, T is left ventricular wall thickness, R is radius of so if radius of the left ventricular chamber ) in LVH as there is hypertrophy of cardiac muscle, the wall thickness increases and radius of left ventricular chamber decreases the pressure in the left ventricle increases that may predispose to heart failure
EF = SV/ EDV , As in in diastolic dysfunction; there is improper filling of the ventricle therefore decreasing the END DIASTOLIC VOLUME and hence EF remains unchanged/ normal as seen in this case
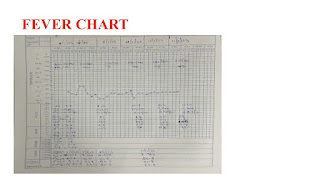
SLIDE NO.12
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.12
There are no fever spikes
SLIDE NO.13
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.13
The diagnosis is cardiogenic pulmonary edema with type 1 respiratory failure with known case of DM type 2 , HTN with CKD
Main treatment points are :
Inj.furosemide 40 mg / IV / twice daily
Tab.Amlodipine 10mg / orally / once daily
Inj. Human Actrapid Insulin/ sub cutaneous / thrice daily
Intermittent CPAP
SLIDE NO.14
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.14
DISCUSSION ON PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CARDIOGENIC AND NON CARDIOGENIC PULMONARY EDEMA
In case of cardiogenic pulmonary edema there is increased pressures in left side of heart and pressure is transmitted to LUNG THROUGH PULMONARY VEINS , in the lung there is increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure ; this leads to increased hydrostatic pressure in the blood capillaries at the alveolar end, there is fluid leak into alveoli and hence there is pulmonary edema but there is intact alveolar epithelial basement membrane & endothelial basement membrane, the fluid collected in the alveoli is purely of trasudative in nature
On the other hand in case of non cardiogenic pulmonary edema for example in cases of pneumonia and ARDS , there is disruption of alveolar epithelial basement membrane & endothelial basement membrane initiated by pro inflammatory mediators IL 1, IL 8 & TNF ALPHA an later further inflammation is mediated by neutrophils which releases proteases and reactive oxygen species this cascade leads to fluid leak in to the alveoli but this time with neutrophil cells,inflammatory mediators, proteins & there are marked infalmmatory changes in the alveoli the fluid collected in the alveoli is of exudative in nature
SLIDE NO.15
SPEAKER NOTES FOR SLIDE NO.15
THE CONCLUSION OF MY PRESENTATION IS , WE NEED TO DO LONGITUDINAL STUDY THROUGH REGULAR FOLLOW UP RATHER THAN CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY TO COME TO A CONCLUSIVE DIAGNOSIS , THIS WAY THERE IS LEARNING FOR THE DOCTOR TREATING THE PATIENT AND PATIENT COULD FEEL BETTER SYMPTOMATICALLY. SO BY THIS THERE IS EVEN BETTER DOCTOR PATIENT RELATIONSHIP















Comments
Post a Comment